Transformer Ground Size Chart | Best Ground Wire Sizing Guide for Safe Electrical Installations
Correct grounding is a critical part of transformer installation, and using a reliable transformer ground size chart helps engineers and electricians select conductors that maintain safety and compliance. When grounding is undersized or incorrectly selected, fault current paths become unreliable, equipment protection weakens, and personnel safety can be compromised. This guide explains how to use a transformer ground size chart, what factors influence conductor selection, and how to interpret sizing tables in practical field conditions.
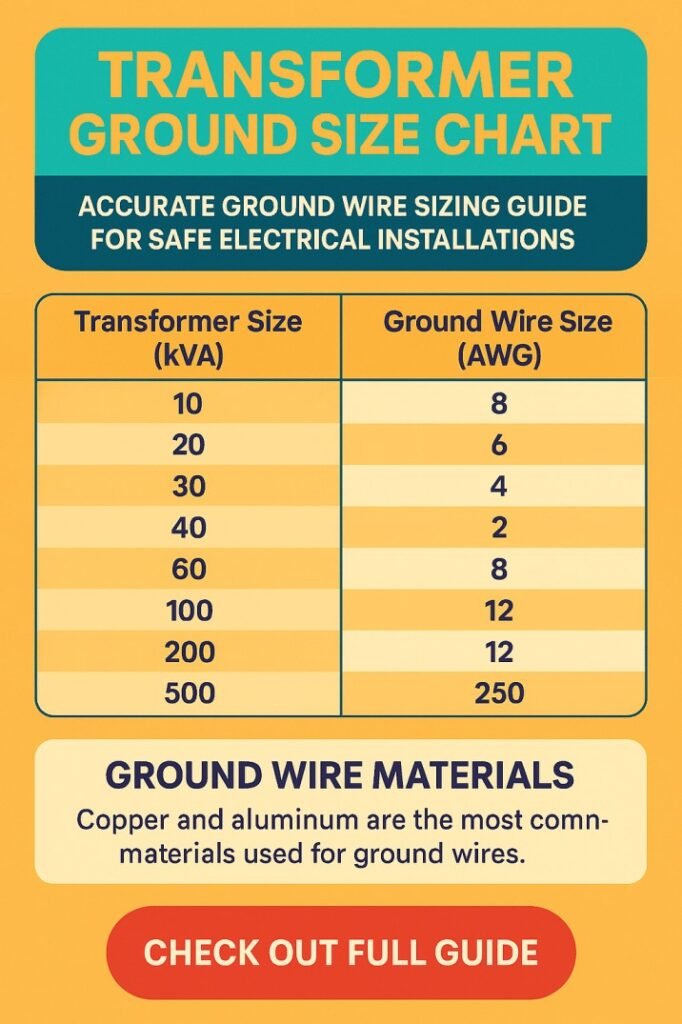
Table of Contents
Transformers serve as essential nodes in power distribution, and grounding provides a controlled path for fault energy and lightning surges. Whether working with distribution transformers, dry-type units, or pad-mounted equipment, applying the transformer ground size chart correctly ensures the grounding electrode conductor and bonding connections perform as expected. The information below presents practical sizing references and real-world considerations to support safe electrical installations.
Understanding the Purpose of a Transformer Ground Size Chart
A transformer ground size chart provides a structured reference for determining conductor sizes based on system parameters. These parameters include transformer rating, primary voltage level, available fault current, and applicable electrical standards. Instead of guessing or oversizing arbitrarily, installers use the transformer ground size chart to align conductor capacity with the potential energy involved in ground faults.
Know more about Transformer Cooling Methods: ONAN, ONAF, OFAF & More
Grounding conductors must withstand short-circuit current long enough for protective devices to clear the fault. Thermal limits of copper or aluminum, insulation ratings, and mechanical durability all influence sizing. A transformer ground size chart simplifies these calculations by summarizing engineering principles into practical values that match common installation scenarios.
Additionally, grounding systems must maintain low impedance paths to earth. This requirement supports overcurrent device operation and voltage stabilization. Applying the transformer ground size chart in conjunction with soil resistivity testing, electrode selection, and bonding verification ensures consistent performance.
Key Factors That Influence Ground Wire Selection
Several technical aspects affect how values are chosen from a transformer ground size chart. Transformer capacity is often the first consideration because higher kVA ratings typically correspond to higher available fault current. Voltage level also impacts insulation coordination and conductor spacing. Environmental conditions such as soil type, moisture content, and corrosion risk must be evaluated alongside chart recommendations.
Explore all about Transformer Bond Sizing
Material choice is another major factor. Copper offers superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, while aluminum provides lighter weight and cost advantages. The transformer ground size chart generally distinguishes between these materials because equivalent current capacity requires different cross-sectional areas.
Protective device clearing time also matters. Fast-acting breakers allow smaller grounding conductors compared to slower clearing systems. Installation methods such as direct burial, conduit routing, or equipment bonding affect heat dissipation and mechanical stress. Reviewing all these elements while referencing the transformer ground size chart produces more reliable grounding solutions. Find Transformer calculators here
Transformer Ground Size Chart Reference Table
The following table presents typical copper grounding conductor sizes aligned with common transformer ratings. These values represent widely applied engineering practices and provide a practical starting point for planning. Final selection should always consider local codes and project specifications.
| Transformer Rating (kVA) | Suggested Ground Conductor Size (Copper AWG) | Typical Application Context |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 8 AWG | Small distribution or control transformers |
| 50 | 6 AWG | Light commercial installations |
| 75 | 4 AWG | Equipment rooms or service feeders |
| 100 | 4 AWG | Industrial auxiliary loads |
| 150 | 2 AWG | Medium plant distribution |
| 225 | 1 AWG | Large facility power systems |
| 300 | 1/0 AWG | Manufacturing operations |
| 500 | 2/0 AWG | Substation distribution units |
| 750 | 3/0 AWG | Heavy industrial feeders |
| 1000 | 4/0 AWG | Utility interface installations |
Using this transformer ground size chart as a reference improves consistency when selecting grounding conductors. It also streamlines project documentation and review.
Know all about Transformer Sizing for EV Charger
Aluminum Conductor Alternative Chart
In some installations, aluminum grounding conductors are preferred due to cost or weight considerations. The transformer ground size chart below provides equivalent sizing guidance when aluminum material is used.
| Transformer Rating (kVA) | Suggested Ground Conductor Size (Aluminum AWG) | Typical Application Context |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 6 AWG | Compact equipment grounding |
| 50 | 4 AWG | Commercial panel grounding |
| 75 | 2 AWG | Facility distribution |
| 100 | 2 AWG | Equipment bonding networks |
| 150 | 1/0 AWG | Industrial installations |
| 225 | 2/0 AWG | Process plant systems |
| 300 | 3/0 AWG | Power distribution centers |
| 500 | 4/0 AWG | Substation grounding grids |
| 750 | 250 kcmil | Large industrial feeders |
| 1000 | 350 kcmil | Utility service connections |
Referring to the transformer ground size chart for aluminum ensures electrical equivalence while accounting for conductivity differences between metals.
Know more about Transformers Earthspark Size Chart
Applying the Chart in Real Installations
Reading a transformer ground size chart is straightforward when installation parameters are known. Start by identifying transformer capacity and confirming system voltage. Then check grounding electrode requirements and protective device characteristics. Matching these values to the transformer ground size chart helps determine a suitable conductor size.
Engineers should also verify bonding continuity across enclosures, cable trays, and metallic raceways. The transformer ground size chart addresses conductor selection, but effective grounding depends on the entire network. Periodic testing of resistance and visual inspection further confirms reliability.
During retrofits or expansions, reassessing grounding conductors using the transformer ground size chart prevents mismatches between upgraded equipment and legacy wiring. This approach maintains compliance and improves long-term operational stability. Find all about Transformer Disconnect Sizing
Compliance and Safety Considerations
Regulatory standards define minimum grounding conductor sizes and installation practices. While a transformer ground size chart provides practical guidance, compliance with recognized codes ensures legal and technical acceptability. Inspection authorities often review grounding documentation, making accurate chart application essential.
Safety extends beyond code compliance. Proper grounding reduces touch voltage risk, stabilizes system potential, and supports lightning protection measures. Consulting the transformer ground size chart when designing or modifying installations reinforces these objectives and protects both equipment and personnel.
Know more about Transformer Sizing for Residential Building
Maintenance programs should include verification of conductor integrity and connections. Corrosion, mechanical damage, or loose bonding can undermine system effectiveness even when original sizing matched the transformer ground size chart. Routine monitoring preserves safety margins.
Benefits of Using a Structured Sizing Chart
Using a transformer ground size chart improves efficiency and consistency in project planning. Instead of performing detailed calculations for every installation, technicians can rely on standardized references to guide conductor selection. This method reduces design time and minimizes sizing errors.
Another advantage is improved communication among engineering teams. Documentation referencing a transformer ground size chart provides clarity for procurement, installation, and inspection personnel. It also supports predictable performance outcomes across multiple project sites.
Use our online tool for free Transformer Neutral Current Calculator – Accurate Neutral Current Estimation
From an operational perspective, grounding systems sized through a transformer ground size chart contribute to stable equipment operation and reduced fault impact. Consistent grounding practices ultimately enhance reliability across the electrical network. Test our online tool for free Transformer Full Load Current Calculator – Accurate Load & Current Calculation Tool for Transformers
Conclusion
Selecting grounding conductors without guidance introduces unnecessary risk, making the transformer ground size chart a valuable tool for engineers and installers. By linking transformer capacity with appropriate conductor dimensions, the chart simplifies decisions that influence safety and compliance. Integrating the transformer ground size chart into planning, installation, and maintenance processes ensures grounding systems remain capable of handling fault energy and environmental stress.
Reliable grounding underpins every stable power system, and consistent application of the transformer ground size chart strengthens that foundation. With proper interpretation and integration into broader design considerations, grounding conductor sizing becomes a predictable and dependable aspect of electrical engineering practice.
Start using our online tool today — it’s free Transformer Short Circuit Calculator – Accurate Fault Current & Transformer Protection Tool
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#TransformerGroundSizeChart, #TransformerGrounding, #GroundWireSizing, #EarthingDesign, #ElectricalDesignGuide, #PowerSystemSafety, #NECGrounding, #SubstationDesign, #ElectricalEngineering, #GroundingCalculation