European Earthing System TN-S TN-C-S TT Explained: Key Differences, Safety, and Standards
The European earthing system is a critical aspect of electrical installations across Europe, ensuring safety, equipment protection, and compliance with standards. Understanding the differences between TN-S, TN-C-S, and TT systems is essential for engineers, electricians, and technical professionals. This article explores each earthing system, their unique characteristics, safety implications, and relevant standards. By the end, you will have a clear grasp of which system suits different scenarios and why proper earthing is non-negotiable in European electrical networks.
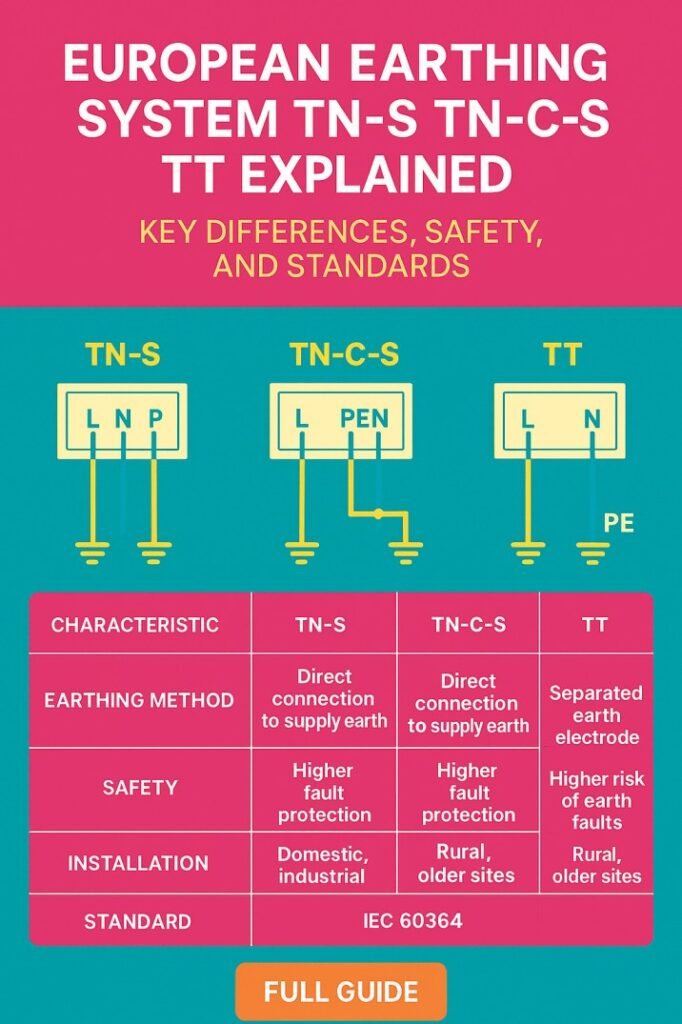
Table of Contents
What is a European Earthing System?
A European earthing system refers to the standardized method of connecting electrical installations to the ground to prevent electric shocks, protect equipment, and stabilize voltages. The system provides a defined path for fault currents, enabling protective devices like circuit breakers and fuses to operate effectively. The design of earthing varies based on supply type, installation environment, and safety requirements.
The three most common systems used in Europe are TN-S, TN-C-S, and TT. Each system has unique grounding techniques, which determine how neutral and protective conductors are handled, the placement of earth electrodes, and the overall safety approach.
TN-S Earthing System
The TN-S system, also known as Terra Neutral-Separate, is characterized by having separate neutral (N) and protective earth (PE) conductors throughout the installation. This system is widely used in industrial and commercial environments where electromagnetic interference needs to be minimized.
Start using our easy-to-use online tool earthing cable size calculator
Key Features of TN-S:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Neutral & Earth | Separate throughout the installation |
| Safety | Fault currents return via PE conductor |
| Usage | Industrial, commercial, and sensitive equipment |
| Advantages | Reduced electromagnetic interference, higher safety |
| Standards | IEC 60364, EN 50160 |
In a TN-S European earthing system, the PE conductor is connected directly to the main earth electrode at the supply transformer. This ensures that in case of a fault, a protective device trips quickly, reducing the risk of electric shock or fire. TN-S is ideal for locations with high power quality requirements, including hospitals, data centers, and manufacturing facilities. Find more about iec grounding standards
TN-C-S Earthing System
The TN-C-S system, also called Terra Neutral Combined-Separate, combines the neutral and protective functions into a single conductor (PEN) from the supply transformer to a distribution point, after which separate N and PE conductors are used. This system is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings due to cost-effectiveness.
Learn more about earthing cable size as per iec
Key Features of TN-C-S:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Neutral & Earth | Combined (PEN) until distribution, then separated |
| Safety | Protective devices rely on proper PEN continuity |
| Usage | Residential and commercial |
| Advantages | Reduced cabling cost, practical for long distribution networks |
| Standards | IEC 60364, EN 50522 |
While TN-C-S is widely adopted, the combined PEN conductor poses a higher risk if it is damaged or disconnected. Proper maintenance and regular inspection are crucial to prevent hazards like overvoltage on exposed metallic parts.
TT Earthing System
The TT system, or Terra-Terra, features a direct connection of exposed conductive parts to a local earth electrode rather than relying on a supply transformer’s earth. TT systems are commonly used where TN systems are impractical, such as rural areas or locations with unreliable utility earthing.
Dive deeper into instrument earthing iec standard
Key Features of TT:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Neutral & Earth | Neutral from transformer; protective earth via local electrode |
| Safety | Requires fast-acting RCDs for fault protection |
| Usage | Rural areas, remote installations |
| Advantages | Independent from utility earth, enhanced safety in weak networks |
| Standards | IEC 60364-4-41, EN 61140 |
In a TT European earthing system, residual current devices (RCDs) are mandatory to detect leakage currents and disconnect power swiftly. TT is preferred where achieving a low-impedance connection to the supply earth is difficult.
Know all the basics about earth conductor size calculation
Key Differences Between TN-S, TN-C-S, and TT
Understanding the differences between these systems helps in designing safe and efficient installations. The table below summarizes the main contrasts:
| System | Neutral & Earth | Fault Current Path | Main Usage | Safety Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN-S | Separate | Through PE | Industrial & sensitive equipment | Circuit breakers, fuses |
| TN-C-S | Combined until distribution, then separate | Through PEN | Residential & commercial | Circuit breakers, fuses, PEN continuity |
| TT | Local earth electrode | Through local earth via RCD | Rural & remote areas | RCDs essential |
The table highlights that while TN-S provides superior safety and reliability, TN-C-S balances safety with cost efficiency, and TT ensures protection in areas where transformer earthing is not reliable.
Know more about IEC Standard for Earthing System
Safety Considerations in European Earthing Systems
Safety is the primary driver behind the design of the European earthing system. Fault currents must be safely conducted away from equipment and humans to prevent electric shock. Each system requires specific protective measures:
- TN-S: Ensure correct PE conductor sizing, regular testing, and grounding at the transformer.
- TN-C-S: Monitor PEN continuity, use equipotential bonding, and avoid interruptions in combined conductors.
- TT: Use fast-acting RCDs, maintain local earth electrodes, and verify resistance values periodically.
Adhering to these precautions reduces the risk of shock, fire, and equipment damage.
Standards Governing European Earthing Systems
Compliance with international and European standards is mandatory for designing and implementing safe European earthing systems. Key standards include:
- IEC 60364: Electrical installations of buildings, covering earthing arrangements.
- EN 50160: Voltage characteristics in public electricity networks.
- EN 50522: Earthing of high-voltage installations.
- EN 61140: Protection against electric shock.
Explore details on table 250.122 nec
These standards define not only the configuration of earthing systems but also testing procedures, maintenance requirements, and protective device coordination.
Choosing the Right European Earthing System
Selecting the appropriate system depends on various factors, including location, supply reliability, installation type, and cost. TN-S is suitable for sensitive industrial environments, TN-C-S is practical for urban residential networks, and TT is ideal for rural or remote locations.
A careful site survey and understanding of fault current paths, bonding requirements, and protective device ratings are critical to ensuring both safety and compliance.
Conclusion
The European earthing system forms the backbone of electrical safety across Europe. TN-S, TN-C-S, and TT systems each offer unique advantages and are designed for specific applications. While TN-S excels in safety and interference reduction, TN-C-S balances practicality and cost, and TT provides independence in remote locations.
Find all about substation earthing design
Compliance with international standards and regular maintenance ensures that these systems perform reliably and protect both people and equipment. Engineers and electricians must understand these differences thoroughly to implement safe and efficient electrical installations across diverse European environments.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#EuropeanEarthingSystem, #TNS, #TNCS, #TTSystem, #ElectricalEngineering, #EarthingStandards, #PowerDistribution, #SafetyEarthing, #ElectricalCodes, #GridEarthing