Types of VFD: Important Guide to Choosing the Perfect Variable Frequency Drive for Your Needs
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are essential components in modern industrial and commercial systems, offering unmatched efficiency, control, and flexibility for electric motor operations. Understanding the different types of VFD and selecting the right one for your application can lead to significant energy savings, prolonged equipment life, and smoother process management. This ultimate guide explores everything you need to know about types of VFD, their features, benefits, and selection criteria.

Table of Contents
What is a VFD?
A Variable Frequency Drive is an electronic device used to control the speed and torque of an AC motor by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. VFDs are widely used in HVAC systems, pumps, conveyors, and manufacturing machinery. The core advantage of VFDs is energy efficiency, as they allow motors to operate only at the required speed instead of full speed all the time.
Explore the key standards related to VFDs here IEC Standards for Variable Frequency Drives
Key Benefits of Using VFDs
- Energy savings of up to 50% in variable-load applications
- Extended motor life due to reduced mechanical stress
- Precise process control and improved production quality
- Reduced maintenance costs and downtime
- Soft starting and stopping of motors, preventing sudden shocks
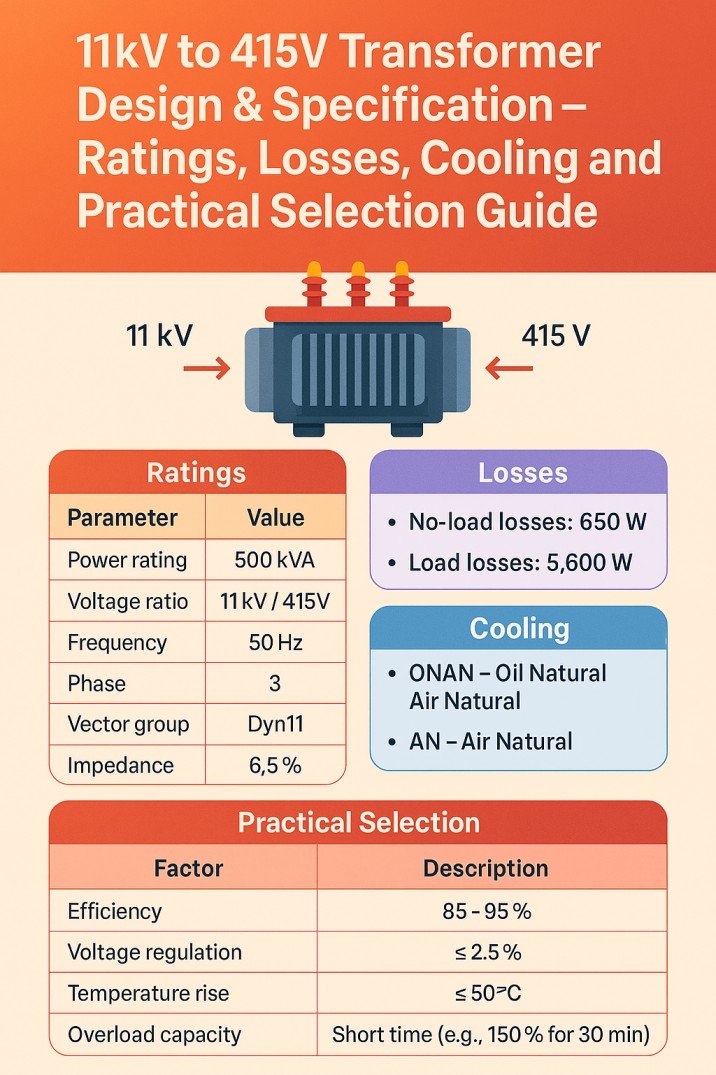
Types of VFD
VFDs are not one-size-fits-all. They come in various types designed for specific applications. Here, we break down the most common types of VFD available in the market.
1. Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) VFD
VSI VFDs are among the most commonly used types of VFD. They convert incoming AC power to DC using a rectifier, then invert it back to variable-frequency AC for motor operation. VSI VFDs are suitable for standard industrial applications and provide reliable speed control for most AC motors.
Learn in detail on vfd overload current setting
Key Features:
- Simple design and cost-effective
- Suitable for constant torque applications
- Limited harmonic distortion
- Easy to maintain
Applications: Pumps, fans, conveyors, and general machinery
2. Current Source Inverter (CSI) VFD
CSI VFDs use a large inductor to provide constant current to the motor. They are less common than VSI drives but excel in applications requiring very precise speed control and torque regulation.
Key Features:
- High reliability for heavy-duty operations
- Excellent for high-inertia loads
- Generates less harmonic distortion compared to VSI in some cases
Applications: Steel rolling mills, hoists, and large compressors
Know more about How to Size a VFD for a Motor. This is an expert Guide for Accurate Selection
3. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) VFD
PWM VFDs are highly efficient and widely used in industrial automation. They generate a variable voltage and frequency output by adjusting the width of pulses in the output waveform.
Key Features:
- Smooth motor operation
- Reduces torque ripple and vibration
- Energy-efficient, even at partial loads
Applications: HVAC systems, robotics, packaging machinery
4. Servo VFD
Servo VFDs are designed for high-precision applications where positioning accuracy is critical. They combine the functionality of a VFD with a feedback system that monitors the motor’s performance.
Key Features:
- Highly precise speed and position control
- Fast response for dynamic loads
- Advanced motor protection
Applications: CNC machines, robotics, and assembly lines
Find the cheapest Variable Frequency Drive Repairing Services in USA
5. Closed-Loop VFD
Closed-loop VFDs use feedback from sensors to monitor motor speed or torque and adjust output accordingly. This type ensures optimal performance even under variable load conditions.
Key Features:
- Superior load handling
- Enhanced motor protection
- High efficiency in complex systems
Applications: Cranes, elevators, and conveyors with variable loads
6. Open-Loop VFD
Open-loop VFDs operate without feedback from the motor, relying on pre-set parameters to control motor speed. While less precise than closed-loop systems, they are simpler and more affordable.
Key Features:
- Cost-effective for less critical applications
- Easy to install and maintain
- Sufficient for constant load systems
Applications: Pumps, fans, and HVAC systems
Having a faulty VFD? Need repairing facilities the you must know Variable Frequency Drive Repairing Services Cost
How to Choose the Right VFD
Selecting the right VFD depends on several factors. Here is a step-by-step approach:
Step 1: Determine Motor Type and Load Requirements
- Identify whether your motor is constant torque, variable torque, or high-inertia load.
- Calculate the required horsepower or kilowatt rating.
Step 2: Consider Application Type
- Match the VFD type to your application’s precision needs.
- Closed-loop VFDs are ideal for dynamic loads, while open-loop works for steady loads.
Step 3: Check Power Supply Compatibility
- Ensure the VFD matches your system’s voltage and phase (single-phase or three-phase).
Step 4: Evaluate Environmental Conditions
- Some VFDs are designed for harsh industrial environments.
- Consider IP rating and cooling requirements.
If you are troubleshooting VFD then this guide will certainly help What are Common VFD Troubleshooting Tips?
Step 5: Review Advanced Features
- Look for built-in protections like overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal monitoring.
- Some VFDs include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for automation integration.
Step 6: Calculate Energy Savings
- Estimate potential energy savings to justify investment.
- Variable torque applications benefit the most from VFDs.
Comparison Table of Common Types of VFD
| Type of VFD | Key Features | Ideal Applications | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| VSI | Simple, reliable, moderate harmonics | Pumps, fans, conveyors | Low-Medium |
| CSI | Precise torque, heavy loads | Steel mills, hoists, compressors | High |
| PWM | Smooth operation, energy-efficient | HVAC, robotics, packaging | Medium |
| Servo | High precision, fast response | CNC machines, robotics | High |
| Closed-Loop | Optimized for variable loads | Cranes, elevators, conveyors | Medium-High |
| Open-Loop | Simple, cost-effective | Pumps, fans, HVAC | Low |
Know more about Top 15 Variable Frequency Drive Manufacturers in USA
Maintenance Tips for VFDs
Proper maintenance can extend the life of a VFD significantly:
- Keep the VFD and motor clean from dust and debris
- Ensure adequate ventilation and cooling
- Check electrical connections regularly
- Update firmware when available
- Inspect capacitors and power electronics periodically
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using a VFD not rated for your motor type
- Ignoring harmonic distortion effects on the electrical network
- Overloading the drive beyond its rated capacity
- Skipping proper grounding and surge protection
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of VFD is crucial for optimizing motor performance, energy efficiency, and process control. From VSI and CSI to PWM, servo, closed-loop, and open-loop drives, each type offers unique advantages tailored to specific industrial needs.
Use our online tool VFD Selection Calculator: Easy & Accurate Drive Sizing for Maximum Efficiency
By carefully considering application requirements, load types, and operational environments, you can select the perfect VFD that maximizes performance, reduces costs, and ensures long-term reliability. Investing in the right VFD today not only improves your system efficiency but also pays off in energy savings and reduced maintenance for years to come.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub