Current in Parallel Calculator – Accurate Tool for Parallel Circuit Analysis
Understanding Current in Parallel Circuits
In electrical circuits, a parallel circuit allows current to split and flow through multiple branches. Unlike a series circuit, where current remains the same, in a parallel circuit, the total current is the sum of individual branch currents. To determine the current in each branch, we use the current in parallel calculator, which simplifies complex calculations for engineers, electricians, and students.
Table of Contents
How Does a Current in Parallel Calculator Work?
A current in parallel calculator uses Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) to determine how current divides among parallel resistors. The formula follows:
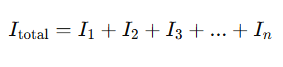
Where:
- Itotal is the total current from the power source
- I1,I2,I3, etc., are the individual branch currents
The current flowing through each branch depends on resistance and the applied voltage using Ohm’s Law:
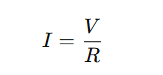
If multiple resistors are connected in parallel, the total equivalent resistance is calculated as:
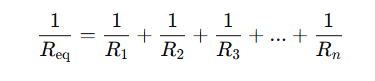
Once Req is determined, the total current can be found using:
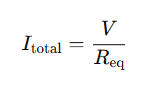
This is how a current in parallel calculator simplifies the process, providing instant and accurate results.
Importance of Current in Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are common in residential wiring, industrial applications, and electronic circuit design. The main advantages include:
- Independent Branch Operation: If one component fails, others remain functional.
- Lower Equivalent Resistance: Parallel connections reduce total resistance, increasing total current flow.
- Voltage Consistency: All branches receive the same voltage, ensuring uniform power distribution.
Applications of Current in Parallel Calculation
Household Electrical Wiring
Most homes use parallel wiring for outlets, allowing multiple devices to operate independently. A wiring size calculator helps determine the correct wire gauge for such installations.
Electronic Circuits
Parallel circuits are essential in power distribution boards, LED arrays, and voltage dividers for maintaining specific voltage levels across circuit components.
Battery Banks in Renewable Energy
Parallel connections are used in battery storage systems to increase total current capacity while maintaining the same voltage.
Current Divider Formula in Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, the current divider formula helps calculate the current flowing through each resistor:
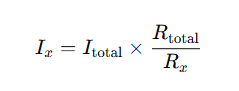
Where:
- Ix is the current through a specific resistor
- Itotal is the total circuit current
- Rtotal is the equivalent resistance of all branches
- Rx is the resistance of the individual branch
This formula is fundamental in current in parallel calculator tools, enabling engineers to analyze complex circuits quickly.
Voltage Divider and Its Relation to Parallel Circuits
A voltage divider is another essential concept in circuit analysis. It allows voltage to be divided among components based on resistance. The voltage divider formula is:
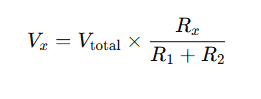
Where:
- Vx is the voltage across a resistor
- Vtotal is the total applied voltage
- Rx is the resistor in question
- R1+R2 is the total series resistance
Although a voltage divider is primarily used in series circuits, understanding it is crucial when designing parallel networks where voltage remains constant across branches.
Voltage Drop and Parallel Circuits
When analyzing parallel circuits, it is important to consider voltage drop across resistors. A voltage drop on resistor calculator determines how much voltage is lost due to resistance. In a parallel circuit:
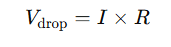
Since all branches in a parallel circuit receive the same voltage, voltage drop calculations become simpler compared to series circuits.
Wire Gauge Selection for Parallel Circuits
Choosing the correct wire gauge ensures efficient current distribution. A wire gauge conversion calculator helps determine the appropriate wire size based on:
- Current carrying capacity
- Voltage drop considerations
- Safety regulations
Incorrect wire selection can lead to overheating, voltage loss, and circuit failure.
Practical Example – Using a Current in Parallel Calculator
Scenario:
A circuit has a 12V power source and three resistors in parallel:
- R1=10Ω
- R2=20Ω
- R3=30Ω
Using the parallel resistance formula:
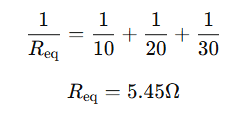
Using the current divider formula:
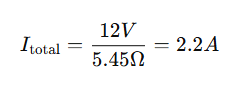
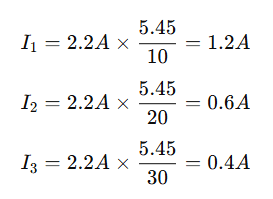
The current in parallel calculator instantly provides these values, eliminating the need for manual calculations.
Why Use a Current in Parallel Calculator?
- Saves Time: Instantly calculates complex parallel circuit parameters.
- Eliminates Errors: Reduces manual calculation mistakes.
- User-Friendly: Engineers, students, and electricians can easily use it.
Using a current in parallel calculator, along with tools like a wiring size calculator, voltage drop on resistor calculator, and wire gauge conversion calculator, makes electrical planning more efficient.
Conclusion
A current in parallel calculator is essential for analyzing parallel circuits efficiently. It simplifies calculations related to current division, total resistance, and individual branch currents. Understanding related concepts like voltage divider, current divider formula, and voltage drop enhances circuit design accuracy.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
CurrentCalculator, #ParallelCircuit, #ElectricalEngineering, #OhmsLaw, #ElectricCurrent, #ParallelResistors, #CircuitAnalysis, #ElectronicsCalculator, #ElectricalFormulas, #PowerCalculation, #VoltageDivider, #OhmsLawCalculator, #CircuitDesign, #ElectricalTools, #EngineeringMath