How to Determine Electrical Service Size
Understanding how to determine electrical service size is crucial for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems. Electrical service size impacts safety, efficiency, and compliance with codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC). Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading an existing system, this guide will walk you through each steps.

Why Knowing How to Determine Electrical Service Size Is Important
The electrical service size is the total amount of electrical power that can be safely delivered to a property. Choosing the correct size prevents overloads, tripped breakers, and fire hazards. Oversizing wastes money. Undersizing puts your equipment and safety at risk.
Determining the right size involves calculating the total expected electrical load and comparing it with service panel ratings, utility guidelines, and NEC requirements like electrical service size calculator.
How to Determine Electrical Service Size: A Step-by-Step Guide
To determine the correct electrical service size, follow a structured process. The general formula involves calculating the total load and adjusting for safety and diversity factors.
1. Calculate the Total Electrical Load
The first step in understanding how to determine electrical service size is to calculate the total electrical load. This is the total amount of electricity your home or building will need based on all the appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices that will be in use.
The total load is expressed in kilowatts (kW) or amperes (amps). If you are unsure how much power each appliance uses, most devices will have a nameplate that indicates their power consumption.
For residential properties, a general rule of thumb is to sum the wattage of appliances and divide by the voltage (usually 240V for residential systems) to convert watts to amperes. Here’s a simple formula:
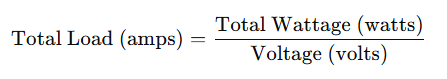
For example, if your appliances use 10,000 watts and your system operates at 240 volts, the total load will be:
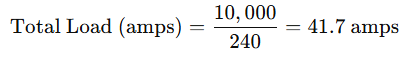
This calculation is the total amperage needed for your property.
2. Apply NEC Load Calculation Rules
The NEC (National Electrical Code) provides guidelines for load calculation, especially for residential properties. The NEC 220-35 load study defines the minimum service size and takes into account the “demand load,” which considers the maximum probable usage of all the electrical appliances over time.
For a typical home, the NEC 220-35 load study offers a load calculation based on square footage, the number of appliances, and the type of service. For example, a small house might need a 100-amp service, while larger homes may require 200 amps or more.
3. Consider Electrical Load Diversity
Not all appliances will be running at full capacity at the same time. That’s why the diversity factor is crucial. The diversity factor reduces the estimated load by accounting for appliances that won’t all be in use simultaneously.
For example, you might not be using your oven, air conditioner, and clothes dryer at the same time. When you calculate electrical service size, you apply this diversity factor to avoid oversizing the system.
A diversity factor of around 1.2 to 1.4 is common for residential buildings.
4. Include Future Loads
If you plan to add new appliances or increase your power demand in the future, it’s wise to consider this when determining your electrical service size. Future-proofing your electrical system helps avoid costly upgrades later.
5. Use an Electrical Service Size Calculator
To simplify this process, many professionals and homeowners use an electrical service size calculator. These calculators take into account various parameters like square footage, appliances, and electrical load types. They can generate a recommended service size with just a few inputs.
For example, an electrical service size calculator might ask for:
- The total square footage of the home or building.
- The number and types of appliances (e.g., air conditioners, water heaters, stoves).
- Additional loads, such as pool pumps or electric vehicle chargers.
Using these inputs, the calculator gives a recommended electrical service size (in amps).
6. Check Local Utility Requirements
Before finalizing your electrical service size, check with your local utility provider. They may have specific requirements or guidelines to ensure your service is compatible with the local power grid.
7. Choose the Right Service Panel Size
After determining the total load and factoring in diversity and future needs, you’ll need to select an appropriate service panel size.
For most residential homes:
- A 100-amp panel is adequate for small homes.
- A 200-amp panel is common for larger homes with more electrical demand.
For commercial properties, panel sizes can range from 200 amps to 800 amps or more, depending on the electrical load.
Service Panel Size Comparison Table:
| Service Panel Size | Typical Application | Recommended Load |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Amps | Small homes or apartments | Up to 24 kW |
| 200 Amps | Average-sized homes, small businesses | 24–48 kW |
| 400 Amps | Large homes, commercial properties | 48–96 kW |
| 800 Amps | Large commercial or industrial properties | 96 kW and above |
8. Consult with a Licensed Electrician
Once you’ve calculated the necessary electrical service size, it’s always a good idea to consult with a licensed electrician. They can verify your calculations, ensure the installation complies with local codes, and guarantee the safety of your system.
Adjusting Service Size for Special Requirements
Certain situations may require adjusting the electrical service size. These can include:
1. High-Energy Demand Devices
Some appliances, such as electric vehicle chargers or large air conditioners, can require significantly more power. If you’re adding high-energy demand devices, you may need to increase the service size.
2. Upgrading for Future Use
When upgrading an electrical system, it’s recommended to oversize the service slightly to account for future energy needs. This reduces the need for another upgrade in the near future.
3. Code Compliance
Ensure that the electrical service size complies with local electrical codes. Following guidelines like the NEC 220-35 load study ensures both safety and legal compliance.
How to Calculate Electrical Load
Knowing how to calculate electrical load is essential for determining the service size. The process involves adding up the wattage of all electrical devices in use at once, then applying safety and diversity factors. Electrical load calculations are often carried out in kW or amps, depending on the system’s requirements.
To calculate electrical load, follow these steps:
- List the wattage of all appliances (use nameplates or manuals).
- Add up the wattage for each appliance you plan to use simultaneously.
- Convert the total wattage to amperes (using the formula mentioned earlier).
- Apply the diversity factor and consider future electrical needs.
Conclusion
Determining the correct electrical service size is essential for both safety and efficiency. Whether you use an electrical service size calculator, apply NEC load study guidelines, or consult a licensed electrician, understanding how to determine electrical service size is key to setting up a reliable and compliant electrical system.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#ElectricalServiceSize, #ElectricalLoadCalculation, #HomeElectricalSystem, #ServicePanel, #ElectricalPlanning, #ElectricalInstallation, #PowerRequirements, #ElectricalDesign, #CircuitBreaker, #ElectricalCode, #ServiceEntrance, #ResidentialElectrical, #ElectricityDemand, #ElectricalUpgrade, #PowerDistribution


