SCADA vs DCS Comparison: Best Professional Guide for Engineers
In the modern industrial landscape, automation systems play a critical role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability. Among the most commonly discussed systems in industrial automation are SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and DCS (Distributed Control System). Both have their distinct strengths, architectures, and applications.
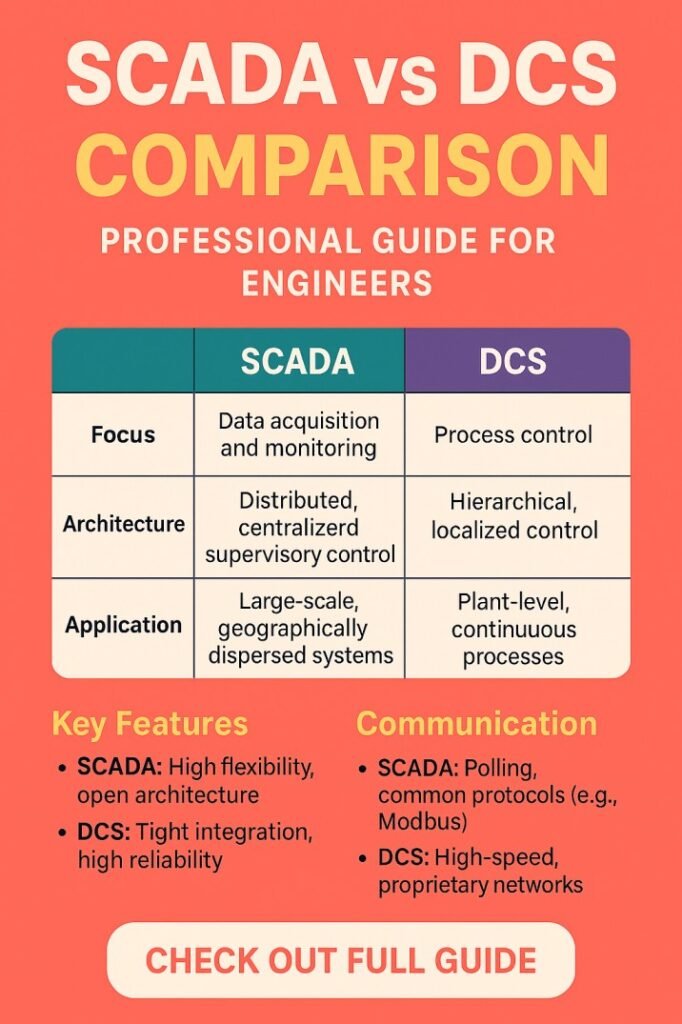
Table of Contents
Understanding the differences and similarities between these systems is crucial for engineers, technicians, and industrial managers when designing or upgrading control systems. This guide provides a comprehensive SCADA vs DCS comparison to help professionals make informed decisions.
Know more about Remote Monitoring with PLC and IoT Integration
Understanding SCADA Systems
SCADA is primarily a monitoring and control system that allows operators to supervise industrial processes from a central location. It collects real-time data from remote equipment using sensors, RTUs (Remote Terminal Units), and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). The collected data is then processed, visualized on human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and used for decision-making or automated control actions.
Key features of SCADA systems include:
- Real-time monitoring and control of remote processes
- Data acquisition and storage for analysis
- Alarm management to detect abnormal conditions
- Support for geographically distributed sites
- Integration with existing PLCs or control devices
SCADA systems are widely used in industries where process control spans large geographical areas, such as water treatment, oil and gas pipelines, electrical grids, and transportation systems.
Know more about Top SCADA Software Platforms for Energy Sector
Understanding DCS Systems
DCS, on the other hand, is designed for process-centric control. Unlike SCADA, which is supervisory, DCS integrates control and monitoring into a single system, often at the plant or factory level. DCS is built to manage continuous processes where precise control over multiple variables is critical, such as chemical production, power generation, and pharmaceuticals.
Key features of DCS systems include:
- Centralized process control with distributed controllers
- High reliability and redundancy for critical operations
- Tight integration between control loops and HMIs
- Advanced process automation and optimization
- Comprehensive alarm and event management
DCS systems are ideal for industries where consistent and continuous control is essential and processes are typically localized within a plant.
SCADA vs DCS Comparison: Key Differences
The choice between SCADA and DCS depends on multiple factors including scale, process type, and control complexity. The following table provides a structured SCADA vs DCS comparison across several critical parameters:
| Feature | SCADA | DCS |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Supervisory control and monitoring | Process control and automation |
| Control Level | High-level (operator intervention required) | Low-level (automated closed-loop control) |
| Process Type | Discrete or batch processes, widely distributed | Continuous processes, typically localized |
| System Architecture | Centralized server with remote terminals | Distributed controllers with centralized HMI |
| Geographical Coverage | Large-scale, remote locations | Confined to plant or site level |
| Data Acquisition | Real-time data from RTUs, PLCs | Real-time process data from local controllers |
| Redundancy | Limited, mostly server-level | High, controllers and network redundancy supported |
| Scalability | Moderate, adding new sites requires integration | High, new controllers can be added seamlessly |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic updates and monitoring | Requires scheduled maintenance, more complex |
| Cost | Generally lower for small to medium applications | Higher due to integration and redundancy features |
This SCADA vs DCS comparison table highlights the primary differences and provides a quick reference for engineers considering system selection.
Know more about HMI vs SCADA: Which System Should You Choose?
System Architecture Differences
SCADA and DCS differ significantly in architecture, impacting how they are deployed and operated.
SCADA Architecture
- Central supervisory computer
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or PLCs at field sites
- Communication network connecting central server and remote units
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI) for operators
- Data historian for logging process information
SCADA’s architecture is designed to handle remote monitoring efficiently, with communication protocols like Modbus, DNP3, and IEC 60870-5 widely used.
DCS Architecture
- Distributed controllers located near the process units
- Central control room with HMI consoles
- High-speed communication buses connecting controllers and HMIs
- Integrated control logic for continuous processes
- Redundant controllers and networks for reliability
DCS architecture emphasizes localized control and high reliability, making it suitable for critical industrial applications where downtime is costly.
Know more about Industrial IoT Sensors in Automation: Cost and Integration
Control Strategy Differences
Control strategy is another area where SCADA and DCS diverge. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right system.
SCADA Control
- Supervisory control with operator intervention
- Relies on PLCs or RTUs for local automation
- Focused on monitoring alarms, trends, and historical data
- Suitable for event-driven or batch operations
DCS Control
- Automated closed-loop control with minimal operator input
- Direct integration of sensors and actuators into controllers
- Continuous regulation of variables like temperature, pressure, and flow
- Supports advanced control algorithms such as PID, fuzzy logic, and model predictive control
This distinction is critical in the SCADA vs DCS comparison because the choice of control strategy impacts process efficiency, safety, and operational costs. Know more about OPC UA vs MQTT: Protocol Comparison for Industrial Control
Applications of SCADA and DCS
Both SCADA and DCS have unique applications based on their architecture and control capabilities.
SCADA Applications
- Electrical power distribution networks
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Water treatment and distribution systems
- Transportation systems, including railways and traffic control
- Remote facility monitoring, such as wind farms or solar plants
DCS Applications
- Chemical and petrochemical plants
- Oil refineries
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Food and beverage processing
- Power generation plants
The SCADA vs DCS comparison highlights that SCADA is often chosen for remote and dispersed operations, while DCS is preferred for centralized, process-intensive plants.
Know more about Modbus Communication Protocol: Master-Slave Explained
Advantages of SCADA Systems
- Remote monitoring allows control of geographically spread processes.
- Cost-effective for industries with multiple sites.
- Flexibility to integrate with existing PLCs and control devices.
- Real-time data visualization aids in faster decision-making.
- Scalable for adding new remote locations.
Advantages of DCS Systems
- High reliability with redundant controllers and networks.
- Precise process control for critical operations.
- Integrated automation reduces operator intervention.
- Advanced alarm management improves safety.
- Seamless integration of new control loops and process units.
Challenges of SCADA Systems
- Limited real-time control capabilities compared to DCS.
- Dependent on communication networks, making it vulnerable to delays.
- Redundancy is often limited to server level.
- Less suitable for processes requiring continuous, precise control.
Know more about PLC Programming Salary 2026 – Experience-Wise Pay, Country Comparison & Skills That Boost Income
Challenges of DCS Systems
- Higher initial investment and installation cost.
- Complexity in maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Less suitable for widely distributed operations.
- Upgrading or scaling can be resource-intensive.
Selection Criteria: SCADA vs DCS
When deciding between SCADA and DCS, engineers should consider the following factors:
- Process type: Continuous or batch vs remote monitoring
- Geographical spread: Local plant vs multiple remote sites
- Control complexity: Simple supervisory vs complex automation
- Budget constraints: Initial cost vs long-term operational benefits
- Reliability needs: Redundant systems required for critical processes
- Integration capabilities: Compatibility with existing hardware and protocols
This approach ensures a data-driven choice, aligning with operational goals and efficiency requirements.
Know more about SCADA HMI Software Cost in 2026 – Pricing, Licenses & Best Value Options
Integration with Modern Technologies
Both SCADA and DCS are evolving to integrate with Industry 4.0 and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) technologies.
- SCADA Integration: Cloud-based monitoring, predictive maintenance, mobile access for operators, and AI-based anomaly detection.
- DCS Integration: Advanced process analytics, digital twins, AI-enhanced process optimization, and seamless connectivity with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems).
These modern enhancements make the SCADA vs DCS comparison increasingly relevant as industries move toward smart manufacturing and digitalization.
SCADA vs DCS Comparison Table for Quick Reference
To simplify decision-making, the following table summarizes the key differences between SCADA and DCS:
| Parameter | SCADA | DCS |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Real-time supervisory | Real-time process |
| Control | Limited, operator-driven | Automated, continuous |
| Scale | Large, distributed sites | Localized plant level |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront |
| Redundancy | Optional, server-level | Built-in, system-wide |
| Installation | Easier, faster | Complex, time-consuming |
| Reliability | Moderate | High |
| Data Handling | Centralized logging | Distributed, process-centric |
| Alarm Management | Moderate | Advanced |
| Process Type | Discrete, batch | Continuous, process-intensive |
Know more about PLC vs DCS: Main Differences for Industrial Automation
Conclusion
Choosing between SCADA and DCS is a critical decision for engineers and plant managers. Both systems have their strengths, and understanding their differences is essential for selecting the right solution. SCADA excels in monitoring geographically dispersed operations and providing flexible, cost-effective supervisory control. DCS offers precise, continuous control with high reliability for critical industrial processes.
By carefully analyzing process requirements, operational scale, and control complexity, engineers can make informed choices that optimize efficiency, safety, and productivity. This SCADA vs DCS comparison serves as a professional guide for selecting the most suitable automation system in today’s industrial landscape.
Investing in the right system ensures long-term operational efficiency, process safety, and technological compatibility with future advancements in industrial automation.
Explore everything about Automation Engineer Certification Cost in 2026 – Fees, Duration & Best Value Programs
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#SCADAvsDCS, #IndustrialAutomation, #ProcessControl, #ElectricalEngineering, #ControlSystems, #NECStandards, #AutomationEngineering, #ProcessSafety, #EngineeringInsights, #IndustrialStandards


