DC Voltage Loss Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding voltage loss in a DC circuit is crucial for ensuring efficient power delivery and avoiding energy waste. A DC voltage loss calculator is an essential tool for determining how much voltage is lost in cables over a given distance due to resistance. This article provides a detailed explanation of DC voltage loss, its causes, calculations, and how a DC voltage loss calculator can simplify the process.
Whether you’re designing a solar power system, sizing cables for a motor, or troubleshooting voltage issues, this guide will give you all the necessary details to optimize your system’s performance.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
What Is Voltage Loss in DC Circuits?
Voltage loss, often referred to as voltage drop, occurs when electrical current flows through a conductor, and resistance within the cable reduces the voltage available at the load end. This phenomenon can result in inefficient operation of devices, especially in low-voltage DC systems like solar panels or battery-powered systems.
The formula for calculating voltage loss is based on Ohm’s Law, which states:
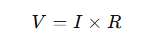
Where:
- V: Voltage loss (in volts)
- I: Current (in amperes)
- R: Resistance of the conductor (in ohms)
Why Use a DC Voltage Loss Calculator?
Manually calculating voltage loss can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially in systems with long cable runs or multiple variables like cable material, length, and cross-sectional area. A DC voltage loss calculator simplifies the process by allowing you to input key parameters and instantly get accurate results.
Using a calculator ensures proper system design, prevents excessive energy losses, and helps in selecting the appropriate cable size.
How Does a DC Voltage Loss Calculator Work?
A DC voltage loss calculator requires the following inputs to compute the voltage drop:
- Conductor Material: Copper or aluminum cables have different resistivity. Copper is a better conductor but can be more expensive.
- Conductor Length: The longer the cable, the greater the resistance and voltage loss.
- Current Flow: Higher current results in greater voltage loss.
- Cross-Sectional Area: Thicker cables have lower resistance and hence less voltage loss.
- Operating Voltage: Knowing the system voltage helps in determining if the voltage loss percentage is acceptable.
Conductor Resistance Table (Ohm/km)
Here is a detailed table showing the resistance of conductors in Ohms per kilometer (Ohm/km) against the cross-sectional area (mm²) for both copper and aluminum:
| Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) | Copper Resistance (Ohm/km) | Aluminum Resistance (Ohm/km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.00 | 18.1 | 29.5 |
| 1.50 | 12.1 | 19.7 |
| 2.00 | 9.05 | 14.8 |
| 2.50 | 7.24 | 11.8 |
| 4.00 | 4.55 | 7.47 |
| 6.00 | 3.03 | 5.01 |
| 10.00 | 1.81 | 3.05 |
| 16.00 | 1.13 | 1.91 |
| 25.00 | 0.724 | 1.21 |
| 35.00 | 0.519 | 0.866 |
| 50.00 | 0.362 | 0.609 |
| 70.00 | 0.259 | 0.435 |
| 95.00 | 0.181 | 0.313 |
| 120.00 | 0.151 | 0.260 |
| 150.00 | 0.121 | 0.208 |
| 185.00 | 0.103 | 0.177 |
| 240.00 | 0.0787 | 0.131 |
| 300.00 | 0.0629 | 0.104 |
The values given above are typical resistances for bare conductors of copper and aluminum, at 20°C.
As the cross-sectional area increases, the resistance per kilometer decreases for both materials, which is important for minimizing losses in electrical transmission.
Copper has a lower resistance compared to aluminum, which is why copper is commonly used in electrical wiring where lower resistance and higher efficiency are crucial.
Steps to Use a DC Voltage Loss Calculator
Using a DC voltage loss calculator is simple:
- Input the system voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V, or 48V).
- Enter the current in amps.
- Select the cable resistance.
- Specify the cable length (both one-way and round trip)
The calculator will output the voltage loss, percentage loss, and suggest if the cable size needs adjustment.
To optimize your setup, you may also want to explore other calculators like the Cable Size for Motor Calculator or the Electrical Load Calculator for related calculations.
Example Calculation
Imagine a solar system delivering 30A over a 20-meter copper cable (one-way). If the cable has a cross-sectional area of 10 mm², and the system voltage is 24V:
Determine the resistance: Copper resistance is approximately 0.0175 Ω/mm²/m. For 10 mm² over 20 meters (round trip 40m):
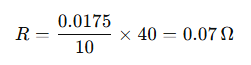
Calculate the voltage loss:
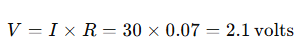
Determine the percentage voltage loss:
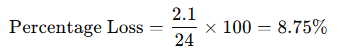
For efficient systems, voltage loss should generally be less than 5%. In this case, a thicker cable would be required.
Benefits of Reducing DC Voltage Loss
Minimizing voltage loss is crucial for ensuring system reliability and efficiency. Some benefits include:
Improved Device Performance: Ensures connected devices receive adequate voltage for optimal operation.
Energy Savings: Reduces energy losses, which is especially important in renewable energy systems like solar panels.
Cost-Effectiveness: Proper cable sizing reduces the need for system overcompensation, saving costs in the long term.
System Longevity: Prevents overheating and wear on cables, extending their lifespan.
Factors Affecting Voltage Loss
Several factors influence DC voltage loss:
1. Cable Material
Copper has lower resistivity than aluminum, making it the preferred choice for reducing voltage loss.
2. Cable Length
Voltage loss is directly proportional to the length of the cable. Keeping cables short reduces loss.
3. Cable Thickness
Thicker cables have lower resistance, which minimizes voltage loss.
4. Current
High current increases the voltage drop. It’s important to consider the maximum load your system will handle.
5. Temperature
Higher temperatures increase cable resistance, leading to higher voltage loss.
Applications of DC Voltage Loss Calculators
1. Solar Power Systems
In photovoltaic (PV) systems, ensuring minimal voltage loss is essential for delivering maximum power to the inverter. A Solar Inverter Sizing Calculator can also be helpful in designing your system.
2. Motor and Industrial Applications
When designing motor circuits, using a Cable Size for Motor Calculator in conjunction with a voltage loss calculator ensures optimal cable selection and motor performance.
3. Battery-Powered Systems
Voltage drop calculations are critical in systems like RVs, boats, and remote battery setups where long cable runs are common.
4. LED and Low-Voltage Lighting
Even small voltage losses can significantly impact low-voltage lighting systems.
Related Calculators for Electrical Design
To optimize your electrical designs further, consider using these calculators:
Ohms Law Calculator: Perfect for basic circuit analysis and troubleshooting.
Voltage Drop Calculator: Ideal for both AC and DC systems to calculate voltage drop over a cable.
Electrical Load Calculator: Helps in calculating total connected load to ensure proper sizing of electrical components.
Tips to Minimize Voltage Loss
- Use shorter cable runs wherever possible.
- Select cables with adequate cross-sectional area.
- Opt for copper cables for better conductivity.
- Avoid overloading circuits to reduce current flow.
- Regularly maintain and inspect cables for damage or wear.
Conclusion
A DC voltage loss calculator is an invaluable tool for ensuring efficient and reliable DC systems. By understanding the factors affecting voltage loss and using the right calculator, you can optimize your system design, save energy, and prolong the life of your equipment.
Whether you’re working with solar panels, motors, or low-voltage lighting, always prioritize accurate calculations. Don’t forget to explore additional tools like the Solar Inverter Sizing Calculator and Voltage Drop Calculator to further refine your designs.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#DCVoltageLoss, #VoltageLossCalculator, #ElectricalEngineering, #VoltageDrop, #ElectricalTools, #CircuitDesign, #PowerEfficiency, #ElectriciansTools, #OhmsLaw, #ElectricalLoad, #VoltageCalculator, #EnergyLoss, #ElectricalFormulas, #WireSizing, #PowerLoss


