How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor
Knowing how to calculate cable size for motor is critical for safe and efficient motor operation. Choosing the wrong cable size can cause voltage drops, overheating, or even fire. This guide gives you everything you need, step-by-step, with standards and technical explanations. The goal is to help you size cables correctly for any motor load.
Importance of Knowing How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor
Cable sizing is more than just picking a wire. It must carry current safely. It must also reduce voltage drop and comply with standards like the National Electrical Code (NEC) and IEC 60204-1. Undersized cables can damage the motor. Oversized cables increase cost.
Knowing how to calculate cable size for motor helps improve safety and performance. It also ensures energy efficiency.
Key Parameters to Consider in Cable Sizing
When learning how to calculate cable size for motor, always consider the following:
- Motor full load current
- Supply voltage
- Length of cable run
- Type of insulation
- Permissible voltage drop
- Ambient temperature
- Installation method (air, buried, conduit)
- Power factor
- Type of load (continuous or intermittent)
How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor Using Formula
To calculate the cable size, start with the full load current of the motor. This is the basis for your calculation. Then apply voltage drop formulas.
Step 1: Find Full Load Current
Use the motor’s rating plate or calculate:
For three-phase AC motors:

Where:
- I = Current in amperes
- P = Motor power in watts
- V = Voltage (line-to-line)
- pf = Power factor (typically 0.8 to 0.9)
- η = Efficiency (typically 0.85 to 0.95)
Step 2: Choose Permissible Voltage Drop
Standards recommend 3%–5% for motor feeders. Keep it low for long distances.
Step 3: Use Voltage Drop Formula

Where:
- VD = Voltage drop in volts
- I = Current
- L = One-way cable length in meters
- R = Cable resistance (Ω/km)
Check if the voltage drop is below your selected percentage of supply voltage. If not, select a bigger cable size.
Example: How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor – 15 kW, 415V
Suppose you have a 15 kW three-phase motor, 415V, 0.88 pf, 90% efficiency, 50m cable run.
Step 1: Find current
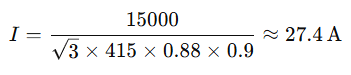
Step 2: Select cable size
From cable manufacturer’s table, 4 mm² copper cable carries about 37 A. But check voltage drop.
Step 3: Voltage drop
Resistance of 4 mm² copper = 4.61 Ω/km


So, 4 mm² cable is suitable.
Cable Size Selection Table Based on Motor Current
| Motor Power (kW) | Voltage (V) | Approx. Full Load Current (A) | Cable Size (Cu, mm²) | Voltage Drop (per 50m, <3%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 415 | 5.2 | 1.5 | Acceptable |
| 7.5 | 415 | 13.5 | 2.5 | Acceptable |
| 15 | 415 | 27.4 | 4 | Acceptable |
| 22 | 415 | 40 | 6 | Acceptable |
| 30 | 415 | 54 | 10 | Acceptable |
Always check manufacturer datasheets for exact resistance values and current ratings.
Cable Insulation Type and Its Role
Insulation affects how much current a cable can carry. For example, PVC-insulated cable has lower ampacity than XLPE. When you calculate cable size for motor, consider the insulation rating.
| Insulation Type | Max Temp (°C) | Current Carrying Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | 70 | Lower |
| XLPE | 90 | Higher |
Higher temperature-rated cables allow smaller sizes for the same current, but cost more.
Standards for Motor Cable Sizing
Here are the key standards that guide how to calculate cable size for motor:
- IEC 60204-1 – Electrical Equipment of Machines
- IEC 60364 – Electrical Installations for Buildings
- NEC 310.15 – Ampacity Tables
- IS 732 – Indian Standard for Electrical Wiring
- BS 7671 – IET Wiring Regulations (UK)
These documents give rules for current capacity, installation types, temperature correction, and voltage drop.
Consider Derating Factors When You Calculate Cable Size for Motor
Cable size depends not only on current but also on environment. Apply derating factors for:
- Ambient temperature: Higher temps reduce ampacity
- Grouping of cables: More cables in a conduit = less cooling
- Soil thermal resistivity (for buried cables)
Derate cable size accordingly to ensure safety.
Motor Starting Current and Cable Sizing
Motors draw higher current during starting. This is called inrush current or starting current, often 6–8 times the full load current. This doesn’t usually affect cable size directly, but you must ensure the cable can withstand this for a short time.
In some cases like DOL (Direct-On-Line) starters, short circuits or protection coordination may require upsizing cables.
Software and Tools That Help in Cable Sizing
Manual calculation is accurate but time-consuming. Several software tools are used for fast and accurate sizing:
- ETAP
- Ecodial (by Schneider)
- Caneco BT
- Amtech ProDesign
- ElectricalOM
These tools follow IEC and NEC rules. They help verify your manual results.
Practical Tips on How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor
- Use motor nameplate current, not rated value from charts.
- For long cable runs, focus more on voltage drop than ampacity.
- Always round up to the next cable size.
- Use manufacturer datasheets for exact cable resistance.
- Check local electrical codes. They may have specific rules.
Summary: How to Calculate Cable Size for Motor
Knowing how to calculate cable size for motor is essential. Start with full load current. Then calculate voltage drop. Consider length, insulation, installation method, and derating factors. Always compare your result with standard tables.
Here is a summary table:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Find motor full load current |
| Step 2 | Choose voltage drop % (usually <3%) |
| Step 3 | Apply voltage drop formula |
| Step 4 | Check if cable rating > motor current |
| Step 5 | Apply derating factors |
| Step 6 | Select next higher standard cable size |
References
- IEC 60204-1: Electrical Equipment of Machines
- IEC 60364: Electrical Installations of Buildings
- NEC 310.15: Ampacity Table
- BS 7671: IET Wiring Regulations
- IS 732: Indian Code for Electrical Wiring
- Schneider Electric – Electrical Installation Guide
- ABB and Havells Cable Catalogs
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
3PhaseMotor, #MotorCableSize, #CableSizeCalculator, #ElectricalEngineering, #MotorWiring, #PowerCalculation, #ThreePhaseMotor, #ElectricalInstallations, #CableSizing, #ElectricalDesign, #MotorLoadCalculation, #VoltageDrop, #CurrentCarryingCapacity, #MotorEfficiency, #ElectricalStandards






